Health and Environmental Impacts of Wastewater Odours
Published : 12 Jul 2025
In wastewater treatment facilities, odour is a direct outcome of volatile substances released during decomposition under septic conditions. The most common odour-causing compounds include hydrogen sulphide, ammonia, mercaptans, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).

Odour: An Indicator of Airborne Chemical Presence
Odour is a characteristic of any gas molecules released, typically the result of volatile substances released into the atmosphere during various treatment processes. Though these emissions may vary in concentration and composition, it triggers a sensory response upon inhalation. Odour causes inconvenience, but that is only the tip of the iceberg.
A high concentration of these gases can injure the respiratory tract and can also cause systemic injury. Most irritant gases are soluble in water and cause sudden irritating symptoms at the surfaces they contact. These symptoms, which include watery eyes, runny nose, and burning of the mouth and face, can serve as warning signs to move away from the exposure.

Causes of Odour Generation
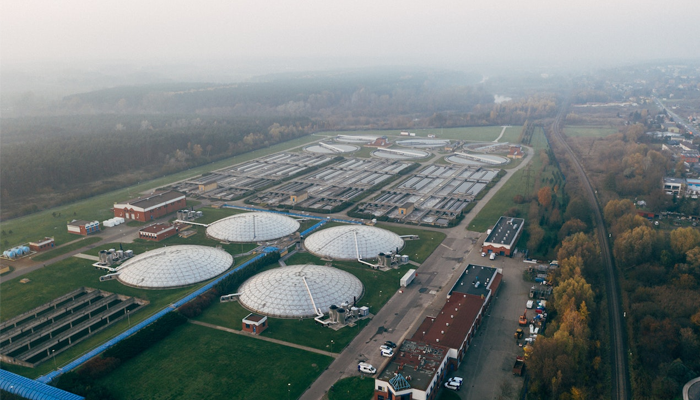
Wastewater treatment plants, produces odour-causing gases due to septic conditions. This is caused by anaerobic bacteria which breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This produces hydrogen sulphide gas which has a characteristic rotten egg smell and is highly corrosive. The septicity occurs as the wastewater sits stagnant which causes anaerobic bacteria to thrive. This is the main reason why odours are generated from the primary treatment tanks of a waste water treatment plant. An efficiently working reaction tank, with abundant of oxygen supply should not produce any smell. In an Effluent Treatment Plant there are different types of gases of varying amounts emitted from various sources, which can only be detected by the odour produced. We can only rely on our sensory organs to detect these odours, despite this being harmful or harmless. What additional impacts can be anticipated?
Factors affecting Lethality
The inhalation of reactive gases and vapours can lead to severe damage of the airways and lung, compromising the function of the respiratory system.
These effects vary from person to person according to
Gas toxicity – It varies for each gas. Thus, abating from exposure to toxic gas molecules is crucial.
Threshold – It is the concentration level which causes damage also varies for each gas.
Gas Concentration – It is the amount of gas present in given space. This is completely unpredictable and detected by humans.
Longer the exposure, higher the impact – Sometimes a lower concentration may not cause immediate effect, but prolonged exposure does.
Impacts of Waste Water Odours
Emissions such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pose potential health risks through various exposure pathways. Inhalation of these gases can lead to irritation of the respiratory tract, including the nose and throat, and may cause cough, discomfort, or chest tightness. Notably, certain compounds can be inhaled without immediate symptoms and still cause internal harm. Dermal exposure may occur when these gases come into contact with the skin, leading to irritation or a burning sensation, with the possibility of absorption into the bloodstream during prolonged exposure. Exposing eye to these substances can result in discomfort, irritation, or chemical injury, and in some cases, absorption through the eye tissues.
As per studies, with less soluble gases, long-term lung damage can occur and cause chronic wheezing and shortness of breath. With prolonged duration of exposure, the resulting harm is severe.
Other than affecting human health, emissions from wastewater odour contribute significantly to air pollution, potentially impacting nearby ecosystems and communities. Due to its acidic nature, compounds such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia not only pose health risks but also lead to the corrosion of infrastructure and hence decline its overall quality. Therefore, effective management and Odour Control are essential to protect both the environment and public well-being.
Prevention of these can be attained by eliminating odourous gas molecules with improved engineering control. Hence, gas molecules causing this odour from any waste water treatment facilities should be captured and treated well with Odour Control Units equipped with appropriate odour removing technology.
Here at AQOZA our team of skilled engineers is equipped with advance technology in gas phase filtration to make lives better.
Want a cost-effective solution for odour? Click here now!
RELATED POSTS
- Know how to choose The Right Odour Control Technology
- Read another related article by PMC
- Not from this industry? No worries — Aqoza offers tailored air quality and gas filtration solutions across multiple sectors. Explore all industries we serve!
- Delve into other solutions provided by AQOZA.